Oak Smart claims to be a leading global asset management service provider. Although it offers stock and cryptocurrency trading services, its transparency and regulatory status are questionable. Users should carefully evaluate the platform before engaging in transactions.
In recent years, the rise of online trading platforms has provided investors with numerous opportunities to enter financial markets. Oak Smart is one of these platforms, claiming to be a leading global asset management company, primarily offering stock and cryptocurrency market trading services. However, despite the platform’s claims on its official website that it is regulated by the U.S. Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), further investigation reveals that the platform fails to provide concrete evidence or clear company information to verify its legitimacy and security.
This article explores Oak Smart’s background, platform risks, and the challenges other investors may face on unregulated or low-transparency platforms. We aim to help potential users better understand the risks associated with this platform and make more informed investment decisions.
Oak Smart’s Background and Regulatory Status
According to its official website (https://www.oaksmart.com/#/), Oak Smart claims to be a leading global asset management company, offering a variety of financial trading services, including stocks and cryptocurrencies. Although the platform’s domain was registered on October 11, 2017, a Google index search revealed that the website only appeared on the internet in 2024. This raises questions about the authenticity of the platform’s operations.
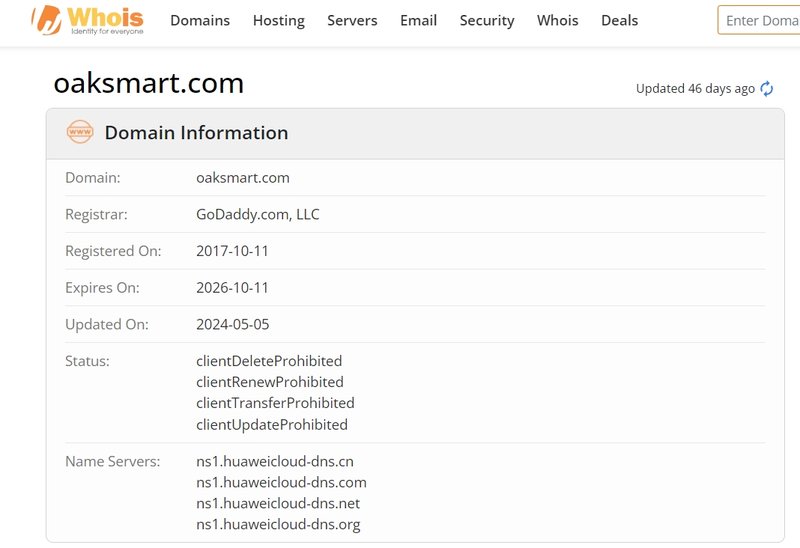
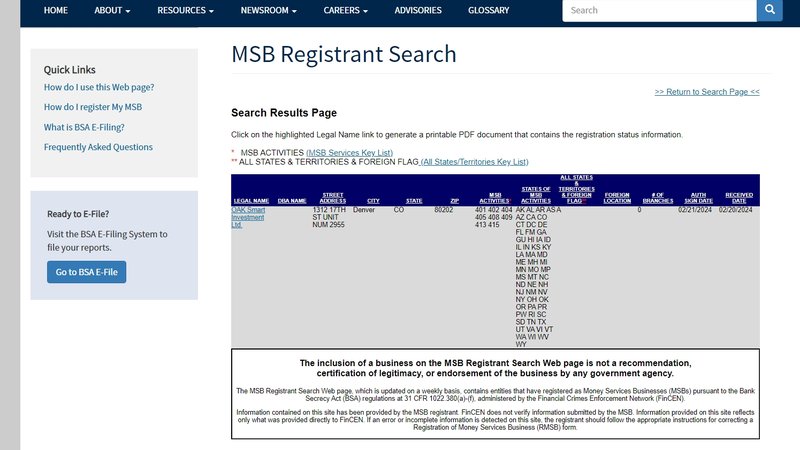
The platform claims to be regulated by the U.S. Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) and lists FinCEN’s website at the bottom of its page. However, it does not clearly state whether it is indeed regulated by FinCEN and fails to provide specific company details for users to verify. While an investigation did uncover a company named “OAK Smart Investment Ltd.” in FinCEN’s database, there is no available evidence directly linking this company to the platform.
It is important to note that FinCEN’s primary role is combating financial crime, not regulating financial derivative trading. Therefore, even though the platform mentions FinCEN, this does not prove that the platform is compliant or subject to strict regulatory oversight in providing trading services. These uncertainties pose potential risks to investors.
Risks of Unregulated Platforms: Real-World Case Studies
Unregulated or low-transparency online platforms pose significant financial and security risks. Many investors have faced frozen funds, withdrawal issues, and platform closures. The following are real-life examples that demonstrate the potential dangers of unregulated platforms.
Case 1: TradeFred’s Fraudulent Activity
TradeFred was an online platform offering forex and contract for difference (CFD) trading that claimed to be regulated in several countries. However, in 2019, the platform abruptly shut down, taking investors’ funds with it. Subsequent investigations revealed that, despite TradeFred’s claims of being regulated, it failed to provide specific regulatory details, leaving investors unable to recover their money.
This case highlights the risks associated with platforms like Oak Smart, which lack transparent regulation. Even if they claim to be regulated, funds may not be protected, especially when investors face withdrawal issues or platform closures.
Case 2: CoinMX’s Illegal Operations
CoinMX was an online cryptocurrency trading platform that facilitated Bitcoin transactions via bank transfers. In 2015, two operators of CoinMX were indicted by the U.S. Department of Justice for bypassing anti-money laundering regulations through false information. CoinMX’s investors not only faced difficulties withdrawing funds but also suffered financial losses when the platform shut down.
This case illustrates how cryptocurrency platforms can become hubs for financial crimes in the absence of regulatory oversight. While Oak Smart claims to offer cryptocurrency trading services, its lack of transparent regulation raises concerns about potential fund safety issues for investors.
Case 3: IronFX’s Frozen Funds Problem
IronFX was a widely used online trading platform that attracted a large number of investors in forex and CFDs. Although the platform was regulated in some countries, it operated in regions where regulations were less stringent. In 2015, many investors discovered that their accounts had been frozen and they could not withdraw funds. The platform claimed the freezes were due to “abnormal account activity,” but many investors were unable to recover their funds through legal channels.
This case demonstrates that even seemingly regulated platforms can pose risks if they lack transparency or proper regulatory oversight. For Oak Smart, which does not provide clear regulatory or fund protection measures, users may face similar risks.
Case 4: QuadrigaCX Cryptocurrency Scam
QuadrigaCX was once Canada’s largest cryptocurrency exchange. However, in 2018, its founder unexpectedly passed away, and it was claimed that he held the private keys to all customer funds. Investors were left unable to recover their money, with total losses reaching $190 million.
The QuadrigaCX case shows that cryptocurrency platforms that lack effective regulatory and fund safeguarding mechanisms can easily lead to misappropriation or irretrievable losses of customer funds. Although Oak Smart offers cryptocurrency trading services, the absence of transparent fund management mechanisms or regulatory protections puts investor funds at considerable risk.
Risks of Trading on Oak Smart
Despite Oak Smart’s claims of offering a wide range of trading products, including stocks and cryptocurrencies, it lacks transparency in several key areas. The platform does not clearly disclose information about its trading software, account types, leverage, spreads, trading fees, or withdrawal processes. This lack of transparency presents potential risks for investors.
Before entering financial markets, investors need to understand the platform’s operational mechanisms and trading rules. Especially with high-risk products like cryptocurrencies and CFDs, the platform’s fund management and regulatory safeguards are crucial for protecting investors.
Case Study: Hidden Dangers of High-Risk Trading Products
In the financial derivatives market, ForexTime (FXTM) faced issues when high leverage ratios led to significant losses for investors during periods of market volatility. Many investors unfamiliar with high-leverage products suffered large losses in a short period, while the platform failed to implement effective risk control measures.
For the Oak Smart platform, while it claims to offer a diverse range of trading products, the lack of transparency regarding leverage ratios and risk control mechanisms means that users may experience uncontrollable losses due to market fluctuations. Investors choosing such platforms must pay special attention to leverage and risk management measures to minimize potential risks.
How to Reduce Risks on Oak Smart
While Oak Smart claims to offer various financial services, its lack of transparency and regulatory oversight means that investors should exercise caution. Here are a few alternative strategies to help reduce risks when using such platforms:
1. Thoroughly Research the Platform’s History and Operations:
Before investing, make sure to deeply investigate the platform’s background and operational history, especially its registration location, years of operation, and user reputation. Search for user complaints or negative feedback to see if the platform has faced operational issues.
2. Avoid High-Leverage Trading:
Unregulated platforms often offer high leverage to attract investors with promises of quick profits. However, high leverage also amplifies potential losses. Investors should adopt a conservative approach when choosing leverage and avoid excessive risk.
3. Prioritize Regulated Trading Platforms:
Rather than trading on a platform with unclear regulation, choose one that is regulated by reputable financial authorities, such as the FCA or ASIC. Regulated platforms offer greater transparency and better legal and financial protection for investors.
4. Consider Using a Demo Account:
Before engaging in real money trading, use the platform’s demo account to test its interface, trading speed, and fund liquidity. This allows you to understand the platform’s operation and potential issues in advance.
5. Maintain a Diversified Investment Strategy:
Even if you choose a highly credible platform, avoid putting all your funds into a single platform or asset. Diversifying your investments can lower the risk associated with individual platforms or markets while increasing overall stability.
By adopting these strategies, investors can reduce financial risks when using Oak Smart or other low-transparency platforms and better protect their financial security.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why can’t Oak Smart’s company information be verified?
While Oak Smart claims to be associated with the U.S. Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), it has not provided clear company names or registration information for users to verify. This raises concerns about the platform’s transparency and legitimacy.
2. Does Oak Smart provide detailed information on trading fees and conditions?
As of now, Oak Smart has not clearly outlined its trading fees, spreads, or leverage ratios. Investors should be cautious of potential hidden fees when using this platform.
3. What risks do investors face when using Oak Smart?
The platform lacks regulatory oversight and transparency in areas such as account types, trading software, and withdrawal methods, which could lead to issues with fund security and trading disputes, making it difficult to recover investments.
4. What should I do if my funds are frozen or if I can’t withdraw?
For unregulated platforms, it is typically difficult for investors to recover frozen or inaccessible funds through legal means. We recommend cautious usage of Oak Smart to avoid investing significant amounts.
5. Does Oak Smart’s claim of being linked to FinCEN mean it’s regulated?
Although Oak Smart references FinCEN, FinCEN is only responsible for combating financial crimes and does not regulate financial trading platforms. Investors should verify whether the platform is overseen by other legitimate financial regulatory bodies.
6. How can I determine if a trading platform is safe?
Choose platforms regulated by reputable authorities (such as the FCA or ASIC) that provide clear company information, fund protection measures, and user safeguards.